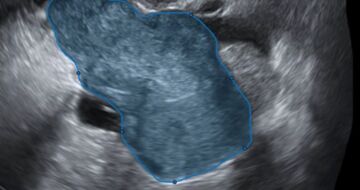

TRACE4BUS™ uses machine learning to analyze US images of suspicious breast masses of subjects at risk to provide the breast mass BI-RADS category
Breast cancer (BC) is one the most frequent malignant neoplasms in women, with 2.3 million women newly diagnosed with this disease and 685 000 deaths worldwide in 2020, according to the World Health Organization.
Breast masses appear to have characteristics at ultrasonography (US) that are helpful in the BC diagnosis to expert operators.
However, Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) guidelines developed so far by the American College of Radiation, are helpful in very low risk group discrimination (0% likelihood of malignancy, BI-RADS 2), while showing limits for masses assigned with an intermediate category (BI-RADS 3-4) and complex in some cases for masses assigned with BI-RADS 5, leading to high ratio of false positives.

TRACE4BUS is our proprietary licensed software that uses machine learning to deeply analyze US images of BC suspicious breast masses of subjects at risks to provide the breast mass BI-RADS category.
TRACE4BUS™ is based on ultrasound (US) image analytics in the breast region, data mining and machine learning classifiers. The software computes a high number of image features representing the morphometric-echogenic pattern of a region of interest contouring a breast mass suspicious of breast cancer (BC) traced by the end-user on a 2-dimensional (2D) US breast image centered on the mass. Scientific evidence has shown that morphometric and echogenic features are different in malignant and benign breast masses and in their adjacent tissues.
When the US image of a BC suspicious breast mass is provided by the user as input to TRACE4BUS™, the suspicious breast mass is automatically classified into one of the three BI-RADS categories associated to their likelihood of malignancy (BI-RADS 3: ≤2% likelihood of malignancy vs BI-RADS 4: 2%-95% likelihood of malignancy vs BI-RADS 5: ≥95% likelihood of malignancy), representing a valid tool to support physicians in the reporting of ultrasound-detected suspicious breast masses.
Download electronic instructions for use
Please, fill the following form to obtain an electronic copy of the instructions of use, including manual, techincal sheet and acquisition protocols, if applicable. An electronic copy of the selected documentation will be sent to your email address.
Your email address and any additional information entered will only be used by DeepTrace to send the requested documentation and to update you about possible future changes in the documentation itself.
Clinical Evidences
A MACHINE LEARNING ENSEMBLE BASED ON RADIOMICS TO PREDICT BI-RADS CATEGORY AND REDUCE THE BIOPSY RATE OF ULTRASOUND-DETECTED SUSPICIOUS BREAST MASSES
Interlenghi, M., Salvatore, C., Magni, V., Caldara, G., Schiavon, E., Cozzi, A., Schiaffino, S., Carbonaro, L. A., Castiglioni, I., & Sardanelli, F. (2022). A machine learning ensemble based on radiomics to predict BI-RADS category and reduce the biopsy rate of ultrasound-detected suspicious breast masses. Diagnostics, 12(1), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12010187 (publication pdf)